Breast Augmentation
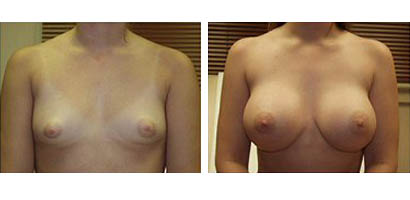
Technically known as “augmentation mammoplasty,” breast augmentation is designed to surgically enhance breast size with breast implants, enlarge small or underdeveloped breasts, reshape breasts lacking in shape and fullness due to pregnancy, nursing or weight loss, balance breasts differing in size and shape, reduce breast that cause a burden or aesthetically unpleasant, and improve self-esteem and personal satisfaction.
Breast Implant Types
There are two manufacturers responsible for the majority of implant sales in the United States - Mentor and Inamed (formerly McGhan). Surgeons have preferences over which company's implants they use - trust your surgeon on company choice.
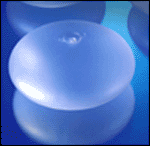 Regarding the implants themselves, all FDA-approved implants are filled with sterile saline - water that contains biological concentrations of salt. If the implant ruptures, the harmless saline will be resorbed by your body.
Regarding the implants themselves, all FDA-approved implants are filled with sterile saline - water that contains biological concentrations of salt. If the implant ruptures, the harmless saline will be resorbed by your body.
Patients undergoing reconstructive surgery may be candidates for receiving the current version of the original (or regular) silicone gel implants - the very implants that were the subject of the short-lived 1992 FDA imposed moratorium. These silicone gel implants may also be available to women undergoing revisions of previous breast augmentations, or women undergoing breast augmentation surgery with breast lift surgery. They remain unavailable to all patients not described by the categories mentioned.
There is a new implant type filled with a cohesive silicone gel that is currently undergoing clinical trials in the United States. If the implant envelope ruptures, the gel has a decreased incidence of leaking into the surrounding tissues when compared with the original (or regular) silicone implants. The consistency of the gel is often likened to gummy bears. Interested in cohesive gel implants? Mentor, Inamed and Silimed manufacture these new implants. Ask your surgeon if he or she participates in one of these studies.
 Regardless of whether you choose a saline or silicone implant, you will also have choices regarding the "feel" and the shape. There are pros and cons with all options.
Regardless of whether you choose a saline or silicone implant, you will also have choices regarding the "feel" and the shape. There are pros and cons with all options.
Smooth Breast Implants VS Textured Breast Implants
The difference between these implant types is intuitive - the surface of one is textured and the other is smooth. Smooth implants move freely in the pocket in which they are inserted. Their shells are thinner when compared to textured implants, and they tend to last longer than textured implants. Textured implants have a higher risk of leaking. Textured implants were originally designed to prevent a complication called capsular contracture - whether they achieve that continues to be debated. Overlying tissue will grow towards the implant and "grab" a hold of the textured surface - which is the intent of the manufacturer so the implant does not move freely in the pocket. However, sometimes the tissue and the implant will move in opposite directions and the tension can cause visible rippling on the skin surface. Rippling does not occur as often with smooth implants.
Round Breast Implants VS Contoured Breast Implants
Implants are basically available in two kinds of shapes: round and contoured. The first is self-explanatory. Contoured implants - sometimes called anatomical implants - were originally designed for reconstructive purposes, and more recently have been used for breast augmentation. They are "bottom-heavy," meaning that because of their conical shape more of the volume is distributed to the bottom when held upright. Contoured implants can turn or flip in the pocket, so they are usually implanted in a textured form to maintain their position.
 Placement of Breast Implant
Placement of Breast Implant
The placement of an implant is commonly referred to as 'overs' and 'unders' which basically refers to the implant being placed over or under the pectoralis muscle.
You will find a lot of information about this subject on the web and in breast augmentation literature, and many surgeons have different and often opposite opinions on the subject. This can create a lot of confusion, especially if you get two different opinions from 2 different surgeons you consult with!
When reading on the internet about implant placement it seems that the majority of women have implants placed partially under the muscle.
This is probably as the majority of women had little breast tissue to begin with so this placement is recommended, but also that many surgeons prefer to use this method. Some surgeons prefer to place implants below the muscle as they feel the risk of capsular contracture is higher with placement above the muscle. However other surgeons say they see no more capsular contracture in their overs vs. unders and perform both placements regularly.
The type of implant chosen can occassionally determine the placement. In most cases it is favourable to place a saline implant and a silicone gel implant under the muscle to decrease the chance of rippling, unless the patient has a good amount of tissue to cover the implant. The newer cohesive gel implant has a lower risk of developing visible ripples therefore either placement
could be recommended to you by a surgeon.
Subglandular Breast Implant Placement
With subglandular placement the implant is placed OVER the pectoralis muscle, under your breast tissue. This placement is considered to be less painful post-surgery as only the skin and fat are cut, with a quicker recovery.
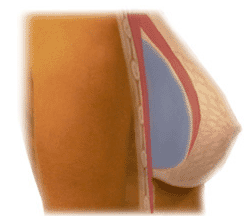 If you have little breast tissue pre-surgery this placement is not recommended as there is more chance you will feel and see rippling of the implant with saline implants. This could be avoided with the new cohesive silicone gel implants.
If you have mild Ptosis (sag) of your breasts pre-surgery this placement may be recommended. If you place the implant below the muscle without a lift with sagging breasts there is a risk of the implant sitting up high with the skin hanging down. However other surgeons think that placing the implant above the muscle could lead to move sagging in the future. It is said that this placement can interfere with the ability to perform a mammography as it prevents complete imaging of the breast tissue. It is also widely reported that there is a higher risk of capsular contracture with subglandular placement, but some surgeons disagree with this.
If you have little breast tissue pre-surgery this placement is not recommended as there is more chance you will feel and see rippling of the implant with saline implants. This could be avoided with the new cohesive silicone gel implants.
If you have mild Ptosis (sag) of your breasts pre-surgery this placement may be recommended. If you place the implant below the muscle without a lift with sagging breasts there is a risk of the implant sitting up high with the skin hanging down. However other surgeons think that placing the implant above the muscle could lead to move sagging in the future. It is said that this placement can interfere with the ability to perform a mammography as it prevents complete imaging of the breast tissue. It is also widely reported that there is a higher risk of capsular contracture with subglandular placement, but some surgeons disagree with this.
Submuscular Breast Implant Placement
With submuscular placement the implant is usually placed partially UNDER the pectoralis muscle. (2/3's of the implant is behind the muscle, the lower 1/3 is not). This placement is considered to be more painful post-surgery as the skin, fat and muscle are cut and the muscle is stretched, with a slightly longer recovery.
If you have little breast tissue pre-surgery this placement is definitely recommended as there is less chance you will feel and see rippling of the implant with saline implants. (However the bottom 1/3 is not covered by the muscle).
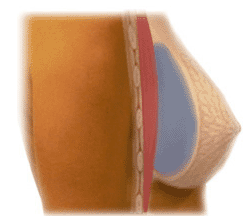 Post-surgery it does take a little longer for the implant to drop and settle than with over the muscle placement, so often the first few months the implant placement can look quite high.
If you have Ptosis (sag) of your breasts pre-surgery this placement may have to be performed with a lift to avoid the implant sitting high and the skin lower.
This placement makes performing a mammography easier, as the implant is separated from the breast tissue by the muscle. Many surgeons consider this placement to lessen the risk of capsular contracture, others disagree.
Post-surgery it does take a little longer for the implant to drop and settle than with over the muscle placement, so often the first few months the implant placement can look quite high.
If you have Ptosis (sag) of your breasts pre-surgery this placement may have to be performed with a lift to avoid the implant sitting high and the skin lower.
This placement makes performing a mammography easier, as the implant is separated from the breast tissue by the muscle. Many surgeons consider this placement to lessen the risk of capsular contracture, others disagree.
This technique can sometimes be referred to as 'partial' unders and seems to be the most common technique performed here in Canada. Some surgeons perform 'complete' unders where the implant is also covered at the bottom by the serratus anterior muscle and anterior rectus abdominus fascia. There are various opinions on this placement depending on which surgeon you talk to....some say this placement invlolves "unnatural" dissection of the breast and the implant sits too high. Others use this technique and think it provides better support
Breast Reduction
Breast reduction (reduction mammoplasty) removes fat, glandular tissue, and excessive skin, resulting in smaller, lighter and firmer breasts that are better shaped in proportion to rest of the body.
Usually breast reduction is performed for physical relief rather than simply cosmetic improvement. Very large breasts that restrict their activities and cause them physical discomfort trouble most patients who have the surgery. Breast reduction can correct a reduction in breast volume after pregnancy or breast that cause personal discomfort.
Surgery is sought by many patients to relieve the physical and painful strain on neck, shoulder and back cased by excessively heavy breasts. A strain that can be severe that it leads to chronic headaches, back deformities, shoulder in dentition breathing problems and a variety of their medical problems.
A breast lift raises and reshapes sagging breasts, by removing excess skin and repositioning the remaining tissue and nipples to improve its appearance. A breast lift can also reduce the size of the areola, the darker skin surrounding the nipple. If a patient’s breasts are small or have lost volume after pregnancy, getting breast implants in conjunction with a breast lift can increase their firmness and size.
Male Breast Reduction
Male Breast Reduction (Gynecomastia), although rarely discussed, enlarged male breasts are a common condition. Gynecomastia affects approximately 40 to 60 percent of men. There is no known cause for gynecomastia, although there has been some correlation with various drugs or medical conditions. Men who feel self-conscious about their appearance are helped with breast-reduction surgery. The procedure removes fat and/or glandular tissue from the breasts, and in extreme cases to removes excess skin, resulting in a contoured chest that is flatter and firmer.